Molecular characterization of Rft1, an ER membrane protein associated with congenital disorder of glycosylation RFT1-CDG
Hirata, E., Sakata, K., Dearden, G.I., Noor, F., Menon, I., Chiduza, G.N., Menon, A.K. (2024) J. Biol. Chem. https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(24)02085-4/fulltext
Phospholipids are imported into mitochondria by VDAC, a dimeric beta barrel scramblase
Jahn, H., Bartoš, L., Dearden, G.I., Dittman, J.S., Holthuis, J.C.M., Vácha, R., Menon, A.K. (2023) Nature Communications 14:8115 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-43570-y
A cholesterol switch controls phospholipid scrambling by G protein-coupled receptors
Menon, I., Sych, T., Son, Y., Morizumi, T., Lee, J., Ernst, O.P., Khelashvili, G., Sezgin, E., Levitz, J., Menon, A.K. (2024) J. Biol. Chem. https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(24)00025-5/fulltext
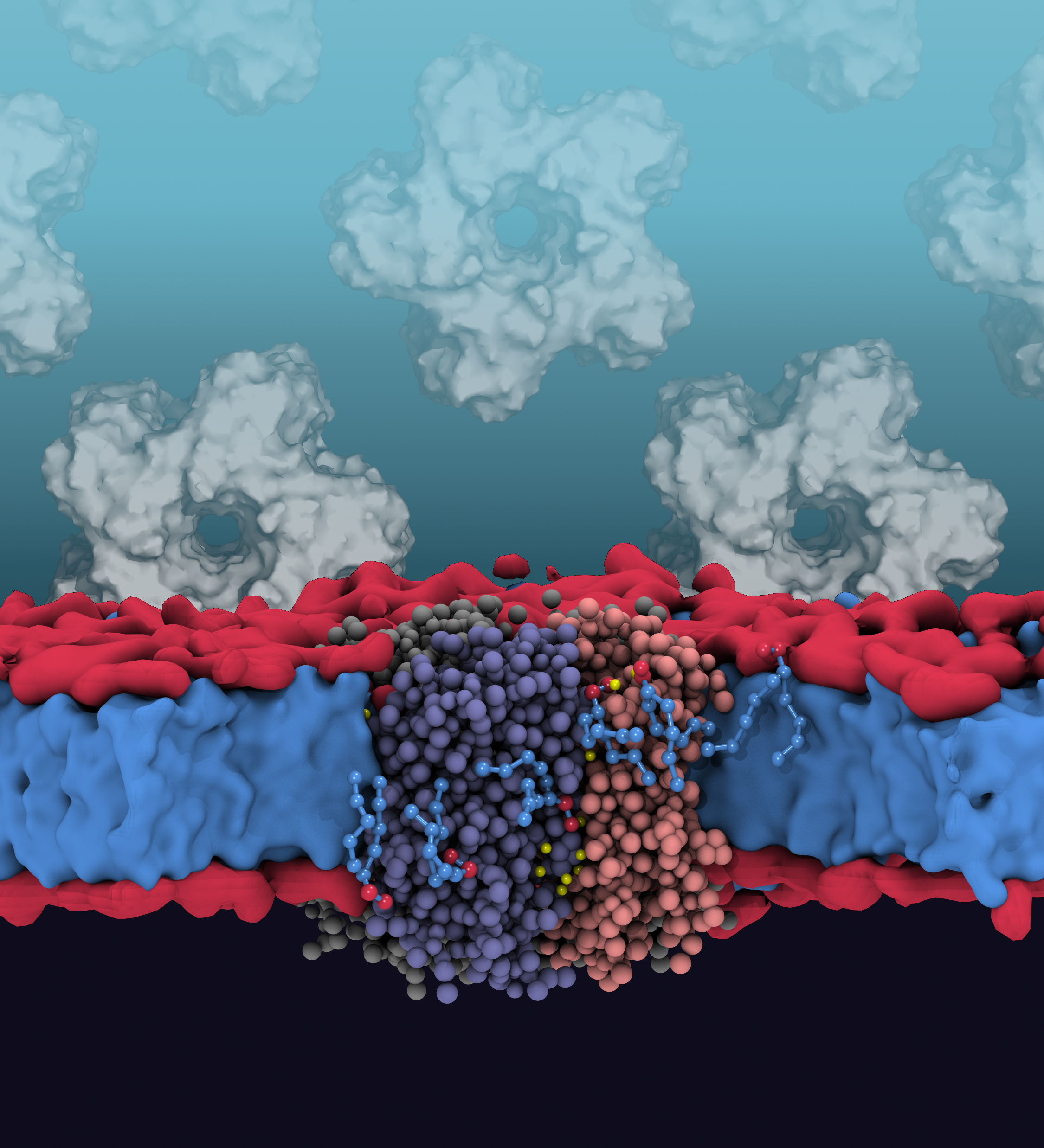
Insertases scramble lipids: Molecular simulations of MTCH2
Bartoš, L., Menon, A.K., Vácha, R. (2024) Structure https://www.cell.com/structure/fulltext/S0969-2126(24)00036-4
Credit card mechanism of phospholipid scrambling
Proposed by Pomorski, Menon (2006) to explain how a membrane protein translocates phospholipids (image by Adam Steinberg). Recent work on GPCR and TMEM16 scramblases supports this model.
Opsins are phospholipid scramblases in all domains of life
Maschmann, Z.A., Hardy, D.E., Menon, I., Webb, J., Menon, A.K., Forest, K.T. (2025) mBio
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mbio.03278-25
Image created by David Hardy, Forest lab, University of Wisconsin-Madison